
IP55, IP65, IP67 and many others are part of a set of protection degrees for electronic devices. Although it has the same acronym, these IPs that we are going to comment on today do not have any relationship with the Internet Protocol Address, the IP.
In the case of this article, the acronym IP stands for Ingress Protect, or Degree of Protection, in Portuguese. Generally, this acronym is accompanied by a numerical code that designates the type of protection present in an electronic device .
However, before we actually start to classify these acronyms, we will know a little about the origins of the IP protection degree.
What are degrees of protection (IP)?
The IP Protection Degree is a set of standards defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which classifies and determines the degree of protection offered by companies against intrusion (body parts such as hands and fingers), dust, accidental contact and water in electronic equipment. It is published by the International Electrotechnical Commission.
This evaluation system is more recognized in European countries, but Brazil is also part, as an integral member of the IEC, therefore, it follows the line of data established by the commission.
In the IP system, the first number identifies the degree of protection against solid objects and the second digit identifies the degree of protection against liquids.
The IP Protection Degree standard aims to ensure more detailed information about the protection capabilities of a given device. For example, instead of using the market definition to claim that a cell phone is waterproof, the IP68 standard specifies that devices that meet this standard can be “submerged in up to 1.5 meters of water for up to 30 minutes.” .”
The IP22 standard generally corresponds to the minimum degree of protection for electrical appliances for domestic use.
Understanding the acronyms of IP protection degree
As stated above, the set of standards for the IP protection degree is formed by numbers that designate the type of protection of the electronic device.
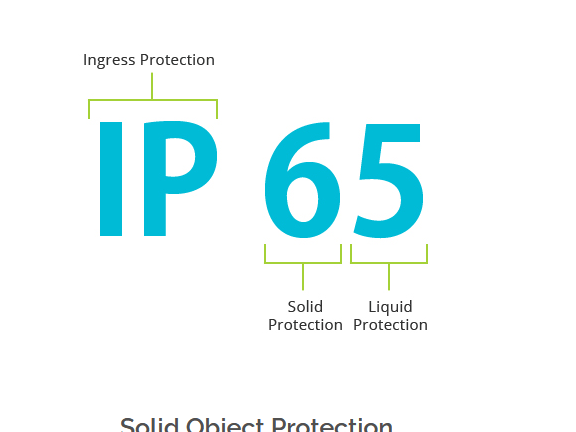
The table below presents all the meanings of the existing abbreviations of the IP protection degree. When there is no protection, the default uses the number 0.
Meanings of the First Numeral – Solid Particles
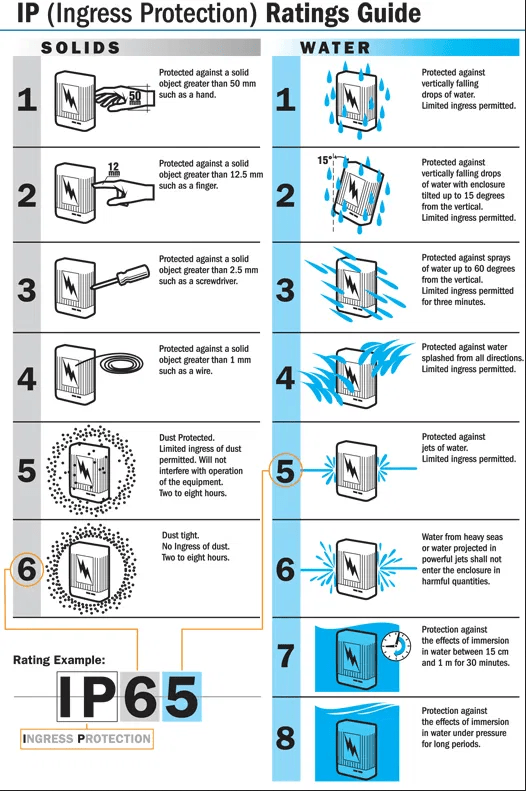
- 0 – Not protected
- 1 – Protection against solid objects with a diameter of 50 mm or more
- 2 – Protection against solid objects with a diameter of 12.5 mm or more
- 3 – Protection against solid objects with a diameter of 2.5 mm or more
- 4 – Protection against solid objects with a diameter of 1.0 mm or more
- 5 – Dust protection
- 6 – Dustproof
Meanings of the Second Numeral – Liquids
- 0 – Not protected
- 1 – Protected against vertically falling drops
- 2 – Protected against drops falling vertically with body inclined up to 15°
- 3 – Protected against water spray
- 4 – Protected against jet of water
- 5 – Protected against water jets
- 6 – Protected against powerful jets of water
- 7 – Protected against temporary immersion in water up to 1 meter for 30 minutes
- 8 – Protected against continuous immersion in water
- 9 – Protection against immersion (for 1 m) and pressure resistant.
- 9K – Protected against water from jets of steam and high pressure
IP54, IP55 and IP65 are some of the most common degrees of protection
In the previous section, we explained what each numeral means and how they are joined to the acronym to define a certain degree of protection.
Remembering that the first number describes protection against solid particles and the second is exclusive for liquids. In addition, when there is still no data on the degree of protection, the letter X is inserted.
Therefore, if the numeral 4 appears in the two digits, like the IP44 degree, it means that the product is protected against solid objects larger than 1 millimeter and against jets of water from all directions.
In the case of IP54, protection against ingress of dust (as listed in the meaning of number 5) is sufficient to prevent a product from operating normally.
In addition, as well as IP44, the product that has the IP54 degree of protection can withstand jets of water from any side.In the case of a product protected against water jets, it is necessary to have at least the IP55 degree, but with the level of protection equivalent to the previous degree against solid objects.On the other hand, the IP65 grade is fully protected against dust and solid objects, in addition to having a nozzle that can withstand powerful jets of water from any angle.
IP67 and IP68 are present in most waterproof cell phones
Waterproof cell phones are very popular in today’s market, but there are some differences in the capabilities of the device due to the degree of protection of the device.
Since the iPhone 7, Apple has introduced liquid-resistant features, but it’s only on the iPhone X that we’ve seen effective protection.
Both the iPhone X and iPhone XR have certifications with the IP67 standard, that is, the devices are fully protected against dust (as well as the IP65 that we discussed earlier) and can be submerged in up to 1 meter of static water for up to 30 minutes.
Samsung‘s Galaxy S10 and iPhone XS Max are rated IP68, which guarantees protection against continuous immersion in water. In addition, cell phones with IP68 protection can stay up to 1.5 m underwater, but, like IP67, only for half an hour.


